Introduction
In today's globe, emergency situations can strike anytime, and being prepared is vital. Among the essential skills that can save lives is cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Teens represent an essential population that can be trained to react properly in emergencies. By outfitting them with CPR training, we not only empower them with life-saving skills however additionally cultivate a culture of readiness and duty. This write-up checks out the importance of mouth-to-mouth resuscitation training for teenagers, what to anticipate in first aid courses, and how these abilities add to their individual growth and community safety.
Understanding CPR Training for Teens: Preparing the Next Generation for Emergencies
What is CPR?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique utilized throughout emergency situations when a person's heartbeat or breathing has quit. It contains breast compressions and rescue breaths that assist keep blood circulation to important organs up until expert clinical help shows up. Understanding the principles of CPR is crucial for teenagers that may discover themselves in emergency situation situations.
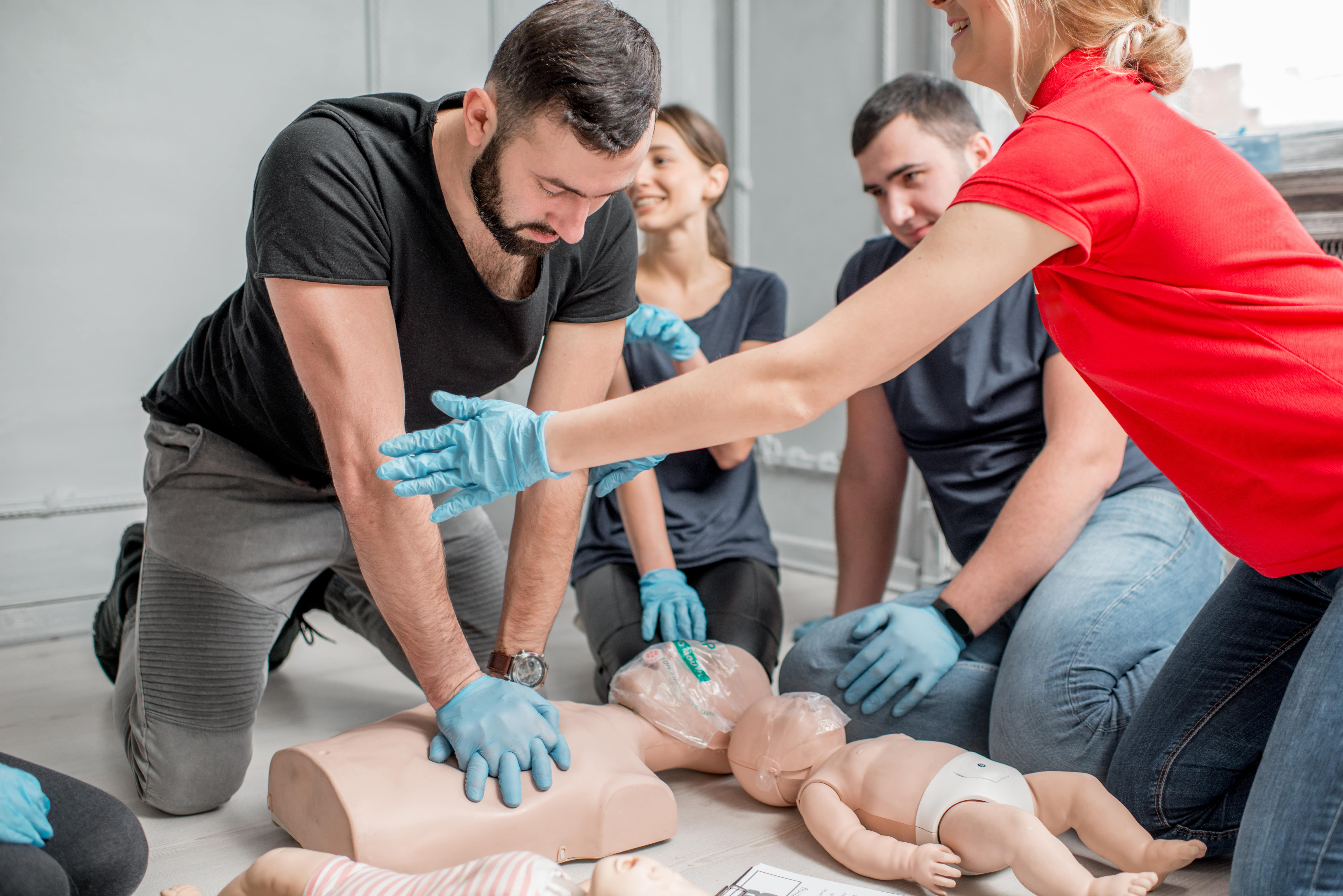
Why Do Teenagers Required CPR Training?
Teens are frequently at celebrations, sports events, and even home events where emergency situations might take place. By learning mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, they end up being proactive members of their area that can act decisively during dilemmas. The ability to perform CPR with confidence can turn a possibly tragic scenario right into one where lives are saved.
Benefits of First Aid Courses for Teens
First aid training courses do more than just teach individuals just how to give instant care; they instill confidence and strengthen problem-solving skills. For teenagers, this experience can construct personality and urge management qualities.
- Empowerment: Expertise of first aid and CPR empowers young people. Confidence Building: Successfully completing a training course gives teenagers with a feeling of achievement. Community Solution: Trained teens can offer in different setups such as institutions or sporting activities teams.
The Framework of CPR Courses for Teens
Course Period and Format
Most emergency treatment training courses are created to fit within a few hours to a couple of days, relying on the depth of training supplied. Generally, a standard first aid course will cover:
- Theory: The concepts behind first aid techniques. Practical Abilities: Hands-on exercise with mannequins or through simulations.
Key Components Covered in First Aid Courses
Understanding Emergency situation Situations- Recognizing when to call for help Assessing the scene for safety
- Performing high-grade upper body compressions Providing rescue breaths correctly
- Learning just how to operate an AED Importance of very early defibrillation
- Techniques for grownups, kids, and infants Recognizing signs of air passage obstruction
- Cuts and scrapes Sprains and fractures
The Importance of Qualification in Emergency Treatment Training
Obtaining Your Emergency treatment Certificate
Completing a first aid course typically finishes in receiving an accreditation that confirms your abilities. This certificate serves numerous objectives:
- It demonstrates proficiency in emergency situation response. Many organizations call for accreditation for participation in particular events.
Keeping Qualifications Current
Just like any type of life ability, it is essential to maintain your expertise up-to-date. Many organizations suggest renewing accreditations every two years.
How Young adults Can Obtain Involved with Emergency Treatment Training
Finding Regional Emergency treatment Courses
Teenagers curious about gaining their first aid certification ought to look into local community centers, colleges, or health organizations that offer licensed programs.
Helpful Resources:
- American Red Cross St John Ambulance Local health centers or health and wellness departments
Online vs In-Person Training Options
With improvements in modern technology, on the internet components have come to be preferred yet may do not have hands-on method essential for really mastering techniques. A mixed strategy-- combining on-line theory with functional sessions-- may be most beneficial.
Creating Awareness Among Peers about Mouth-to-mouth Resuscitation Educating for Teenagers: Preparing the Next Generation for Emergencies
Peer Education and learning Initiatives
Encouraging teenagers to share what they have actually discovered with their friends can amplify the impact of training programs:
- Forming study hall concentrated on emergency preparedness. Hosting workshops at institutions or area centers.
Using Social network as a Platform
Teens today are greatly engaged on social media systems; utilizing these networks can help spread awareness concerning the value of emergency treatment training among peers.
Real-Life Stories That Emphasize the Value of CPR Educating for Teens
Case Research study 1: Saving a Life at College Sports Event
A teen trained in CPR had the ability to save their buddy's life throughout a football suit when he fell down on the area as a result of heart attack. Their quick thinking permitted them to carry out correct upper body compressions until emergency services arrived.

Case Research study 2: Family Emergency Situation at Home
Another example involved brother or sisters who had taken a first aid course with each other. When their younger sibling unintentionally choked on food during supper, they right away knew what steps to take since they remembered their training-- leading them effectively through the emergency.
Frequently Asked Concerns (Frequently Asked Questions) Concerning Teenager CPR Training
1. What age must teenagers start taking mouth-to-mouth resuscitation courses?
The majority of companies advise starting as early as 12 years of ages; nevertheless, younger kids can also learn basic concepts with ideal programs customized to their age group.
2. How much time does it require to finish an emergency treatment course?
Programs normally range from 4 hours as much as 16 hours depending on material depth-- the standard being around 8 hours.
3. Exist any prerequisites before enrolling?
No official requirements exist; however, it's practical if participants have an understanding of basic clinical terms.
4. Will I receive accreditation after finishing my course?
Yes! Upon successful conclusion and passing any kind of essential analyses you'll receive a main emergency treatment certification valid for two years.
5. Can I take these programs online?
Lots of institutions provide hybrid formats integrating on-line theory with called for CPR Course Adelaide sensible sessions kept in individual-- this is recommended by sector standards.
6. Is it essential to restore my qualification periodically?
Yes! Normal recertification ensures your skills remain efficient and current according to current guidelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, equipping young adults with knowledge concerning cardiopulmonary resuscitation (MOUTH-TO-MOUTH RESUSCITATION) through specialized training programs is very useful not only for their growth but also boosts area security generally. With reliable training sources offered-- from local training courses providing detailed guideline on both fundamental first aid strategies as well as advanced life assistance approaches-- it's less complicated than ever before for young individuals anxious concerning making an impactful distinction during emergencies!
As we move on right into an unforeseeable world filled with obstacles needing swift action-- allow us invest our efforts towards informing this next generation so they're prepared not simply academically yet also almost furnished when encountered against real-life circumstances demanding immediate actions like those calling for prompt interventions such as performing effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
